| Uniforme verdeling (continu) |
Kansdichtheid
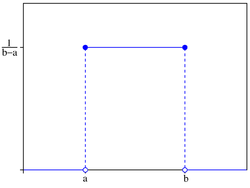 |
Verdelingsfunctie
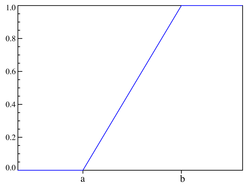 |
| Parameters |  |
| Drager |  |
| Kansdichtheid |  |
| Verdelingsfunctie |  |
| Verwachtingswaarde |  |
| Mediaan |  |
| Modus | N/A |
| Variantie |  |
| Scheefheid |  |
| Kurtosis |  |
| Entropie |  |
Moment-
genererende functie |  |
| Karakteristieke functie |  |
Portaal  | Wiskunde | |
De continue uniforme verdeling is een verdeling op een interval met constante kansdichtheid, wat inhoudt dat er geen voorkeur is voor enige waarde uit dat interval. De kansdichtheid  van de uniforme verdeling op het interval
van de uniforme verdeling op het interval  is daarom constant en wordt gegeven door:
is daarom constant en wordt gegeven door:

Voor elk deelinterval  met lengte
met lengte  is de kans op een waarde daaruit
is de kans op een waarde daaruit  .
.
Opmerking
De uniforme verdeling kan ook beschouwd worden op half open of gesloten intervallen. De functiewaarden van de dichtheid in de eindpunten van het interval doen niet ter zake. In alle gevallen is de verdelingsfunctie dezelfde:

Verwachtingswaarde en variantie
De verwachtingswaarde  van een uniform op
van een uniform op  verdeelde stochastische variabele
verdeelde stochastische variabele  , en de variantie
, en de variantie  , worden gegeven door:
, worden gegeven door:

en

Zie ook
- Uniforme verdeling (discreet)


































